Package GeoSciML/GeologicStructure
GeologicStructures are a configuration of matter in the Earth based on describable inhomogeneity, pattern, or fracture in an Earth Material. The scale of geological structures ranges from microscopic (micron-scale) to megascopic (km-scale). Examples of such inhomogeneities include fractures, mineral grain boundaries, and boundaries between parts of the rock with different particle geometry (texture) or composition. Geologic structure is grounded in relationships between parts of a rock or rock body. As used here, it includes sedimentary structures. The identity of a Geologic Structure is independent of the material that is the substrate for the structure. There are almost always strong dependencies between the nature of the Earth Material substrate and the kinds of Geological Structure that may be present. A disaggregated heap of particles does not have structure, and can only be described in terms of the mineralogy and geometrical character of the constituent particles. Geologic Structures are more likely to be found in, and are more persistent in, consolidated materials than in unconsolidated materials. Properties like "clast-supported", "matrix-supported", and "graded bed" that do not involve orientation are considered kinds of Geologic Structure because they depend on the configuration of parts of a rock body.
Class Summary |
|
| <<FeatureType>> Classes | |
BoundaryRelationship
<<FeatureType>>
|
Defines the two GeologicUnits that make up the relationship described by the Contact |
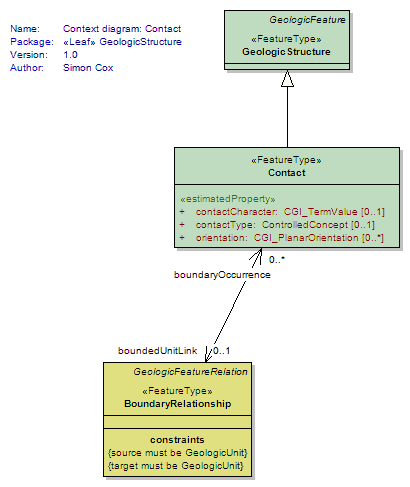
Contact
<<FeatureType>>
|
Very general concept representing any kind of surface separating two geologic units including primary boundaries such as depositional contacts, all kinds of unconformities, intrusive contacts, and gradational contacts, as well as faults that separate geologic units. Permeability of contacts still needs to be modeled; considered out of scope for GeoSciML2. Bedding measured as discrete surfaces in the case that those are the feature of interest (e.g. individual cross set surfaces for paleocurrent analysis) should be represented here. |
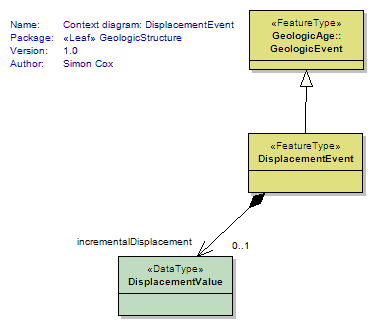
DisplacementEvent
<<FeatureType>>
|
DisplacementEvents are those localised Earth movement GeologicEvents that produce a ShearDisplacementStructure. Subtyping DisplacementEvent from GeologicEvent is intended to allow geologicHistory associations to ShearDisplacementStructure. |
DuctileShearStructure
<<FeatureType>>
|
Parallel-sided zone of localised shearing displacement; may contain sigmoidal mineral-filled veins, locally well-developed cleavage or foliation, wholesale grain size reduction or mylonitisation, or a combination of these features a discrete tabular zone (very thin compared to its along-strike and down dip dimensions) of plastic deformation across which there has been shear displacement. DuctileShearStructure is a map-scale feature. |
Fault
<<FeatureType>>
|
A discrete surface, or zone of discrete surfaces, with some thickness, separating two rock masses across which one mass has slid past the other and characterized by brittle deformation. Fault is a map-scale feature. When observed in outcrop, some faults are just big breccia/gouge zones with no discrete surfaces, sometimes they are breccia/gouge zones bounded by discrete fault surfaces, sometimes a discrete surface in relatively unbroken rock (at the scale of description). |
FaultSystem
<<FeatureType>>
|
A composite structure that is an aggregation of genetically related instances of Faults and/or DuctileShearStructures. A FaultSystem is composed of individually identified and mapped Faults and/or DuctileShearStructures that are considered distinct ShearDisplacementStructures, that generally form overlapping, anastomosing patterns in which, at any point along the fault system, multiple fault strands are identified and each considered important at the scale of description. Displacement and other descriptive data may be assigned at the 'fault segment', 'fault', or 'fault system level'. |
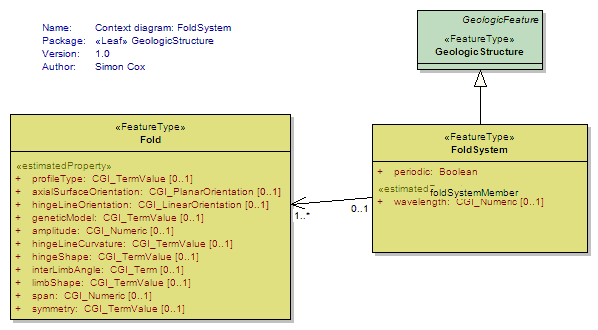
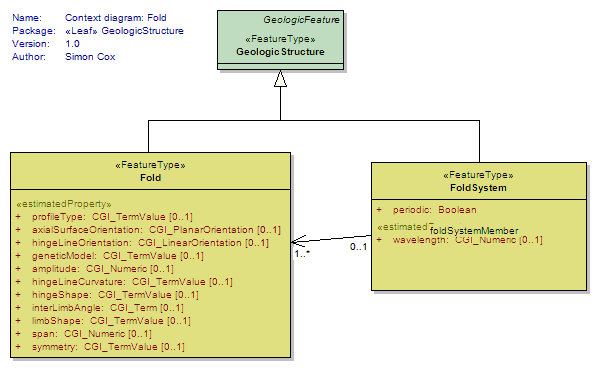
Fold
<<FeatureType>>
|
One or more systematically curved layers, surfaces, or lines in a rock body. Fold denotes a structure formed by the deformation of a GeologicStructure to form a structure that may be described by the translation of an abstract line (the fold axis) parallel to itself along some curvilinear path (the fold profile). Folds have a hinge zone (zone of maximum curvature along the surface) and limbs (parts of the deformed surface not in the hinge zone). Folds are described by an axial surface, hinge line , profile geometry, the solid angle between the limbs, and the relationships between adjacent folded surfaces if the folded structure is a Layering fabric (similar, parallel). |
FoldSystem
<<FeatureType>>
|
A collection of congruent folds (axis and axial surface are parallel) produced by the same tectonic event. Sometimes referred to as a "Fold Train". |
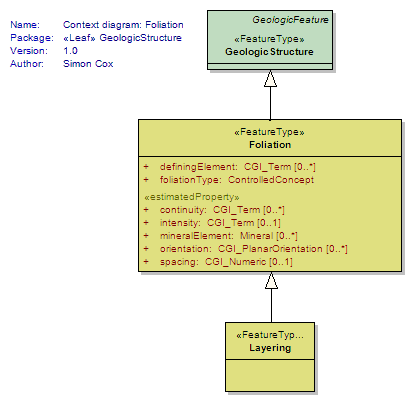
Foliation
<<FeatureType>>
|
A planar arrangement of textural or structural features in any type of rock. Includes any of a wide variety of penetrative planar geological structures that may be present in a rock. Examples include schistosity, mylonitic foliation, penetrative bedding structure (lamination), and cleavage. Following the proposed definition of gneiss by the NADM Science Language Technical Team, penetrative planar foliation defined by layers > 5 mm thick is considered Layering. Bedding as a fabric representing the average orientation of paleodepositional surface should be encoded through the foliationType; might apply to bedding that is layering or a foliation without layering (e.g. clast alignment in amalgamated beds). |
Fracture
<<FeatureType>>
|
Fractures are cracks in the earth surface. If there is no displacement it is a joint. If there is displacement and you are in the brittle zone it is a fault. In the ductile zone, a fracture with displacement with fracture is called a shear. FaultSurface as a separate class is not considered necessary for GeoSciML 2. Recording observations on FaultSurface should be in observation and measurement. The observation needs to be able to distinguish the type of measurement made (PropertyType) |
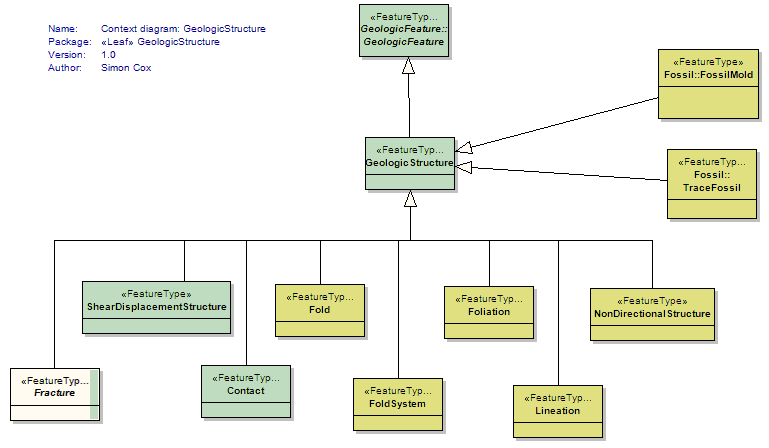
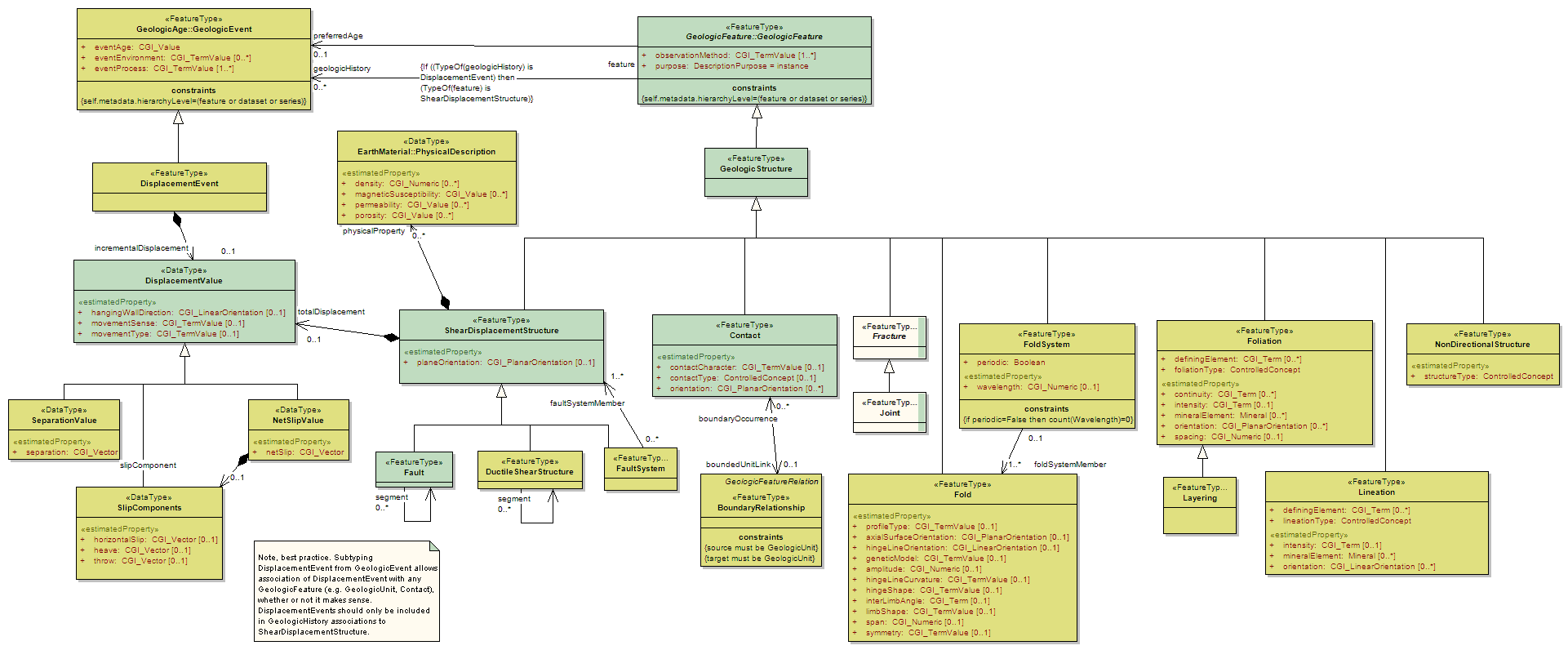
GeologicStructure
<<FeatureType>>
|
A configuration of matter in the Earth based on describable inhomogeneity, pattern, or fracture in an EarthMaterial The identity of a GeologicStructure is independent of the material that is the substrate for the structure. GeologicStructures are more likely to be found in, and are more persistent in, consolidated materials than in unconsolidated materials. Properties like "clast-supported", "matrix-supported", and "graded bed" that do not involve orientation are considered kinds of GeologicStructure because they depend on the configuration of parts of a rock body. Includes: sedimentary structures. In GeoSciML 2.0 Fabric is treated as a class that describes an EarthMaterial (FabricDescription). The general GeologicRelation is used to associate penetrative GeologicStructures with GeologicUnits. |
Joint
<<FeatureType>>
|
Fracture across which there is no displacement at the scale of interest. |
Layering
<<FeatureType>>
|
Planar foliation defined by a tabular succession of layers > 5 mm thick. This definition is based on the proposed definition of gneiss by the NADM Science Language Technical Team, so that the GeologicStructure characteristic of gneiss is layering. The committee discussed the possibility that layering should be considered a kind of foliation, but the majority opinion was that it is a different kind of structure. Kept so that instance documents have a "Layering" tag |
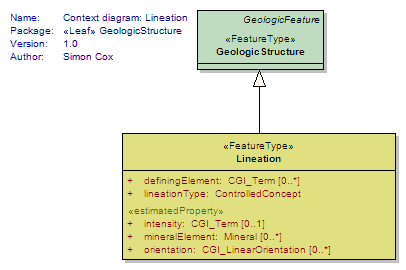
Lineation
<<FeatureType>>
|
GeologicStructure defined by aligned elongate elements. Lineation connotes a pervasive linear structure. Includes: flow lines, scratches, striae, slickenlines, linear arrangements of elongate components in sediments, fold hinges (when abundant and closely spaced), elongate minerals, crinkles, and lines of intersection between penetrative planar structures. Class also includes discrete linear structures like boudin, channel axis, tool marks. |
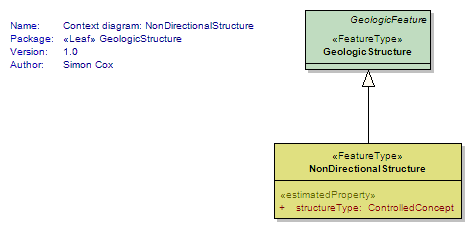
NonDirectionalStructure
<<FeatureType>>
|
Structures present in geology that do not have a preferred orientation Includes small-scale structures that are characteristic of the geologic unit, e.g. herringbone crossbedding, mudcracks, graded bedding, planar lamination, miarolitic cavities, nebulitic structure |
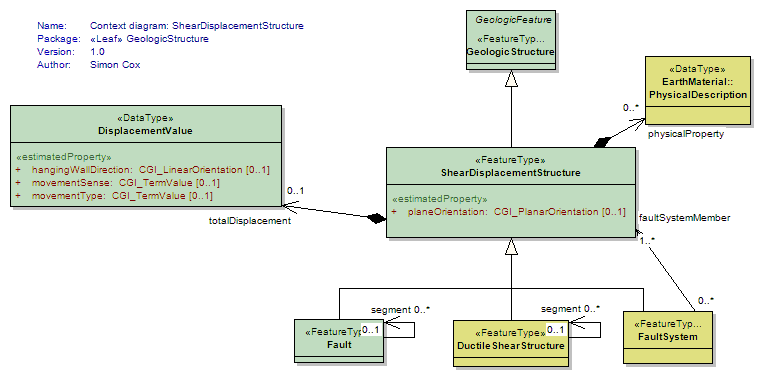
ShearDisplacementStructure
<<FeatureType>>
|
A generalized shear displacement structure without any commitment to the internal nature of the structure (anything from a simple, single 'planar' brittle or ductile surface to a fault system with 10's of strands of both brittle and ductile nature). This surface may have some significant thickness (a deformation zone) and have an associated body of deformed rock that may be considered a DeformationUnit |
| <<DataType>> Classes | |
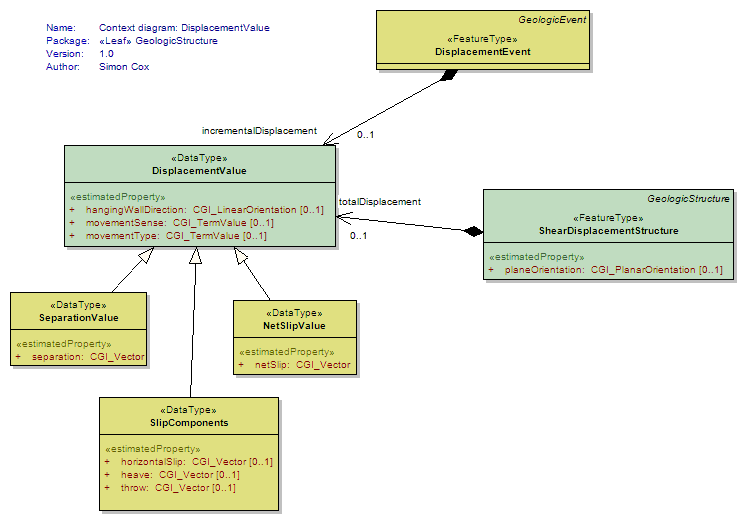
DisplacementValue
<<DataType>>
|
Trying to express the displacement on a fault with respect to a planar approximation of its shape |
NetSlipValue
<<DataType>>
|
The total amount of slip displacement |
SeparationValue
<<DataType>>
|
The amount of separation displacement |
SlipComponents
<<DataType>>
|
representation of slip as vector resolved into components resolved into reference frame in which horizontal axes are parallel and perpendicular to the strike of the fault. |
Tagged Values |
||
| Tag | Value | Notes |
| xsdDocument | geologicStructure.xsd | Description: Relative path to XML Schema document corresponding to this package. |
UML Diagram: Context diagram: FoldSystem
UML Diagram: Context diagram: NonDirectionalStructure
UML Diagram: Context diagram: ShearDisplacementStructure
UML Diagram: Context diagram: Lineation
UML Diagram: Context diagram: DisplacementEvent
UML Diagram: Summary diagram: Geologic Structure
UML Diagram: Context diagram: Contact
UML Diagram: Context diagram: Fold
UML Diagram: Context diagram: DisplacementValue
UML Diagram: Context diagram: Foliation
UML Diagram: Context diagram: GeologicStructure